Gizem Erol (ESR 13) from the Gobbi Group at the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research, in Italy has co-authored a new publication titled “New nanostructures inhibiting human mannose binding lectin identified by a novel surface plasmon resonance assay” and published in Elsevier’s Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
This paper results from an international collaboration involving three other NanoCarb ESRs – Patricia Perez Schmidt (ESR 5), Alessia Pancaro (ESR 11), and Javier Melo DIaz (ESR 6) – and four research groups from CNR SCITEC, VITO and the companies Ludger Ltd, and Midatech Pharma PLC.
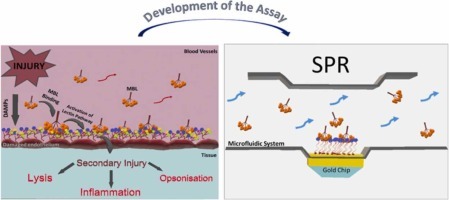
In this paper, a new surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assay was developed and characterized for in vitro screening of inhibitors of the binding of human Mannose Binding Lectin (MBL) to carbohydrate arrays exposed on damaged endothelium. MBL inhibitors have recently been proposed as a promising therapeutic strategy to prevent the progression of tissue damage caused by ischemic events, which is a highly relevant and unmet medical need. Thus, the availability of this new in vitro biosensor-based assay is expected to boost the discovery of MBL inhibitors to be tested later in the more expensive and time-consuming studies in cells and animal models of MBL mediated-injuries. The application of this assay allowed us to identify two novel multivalent mannosylated nanoconstructs, a nine mannose-carrying glycan and, mainly, mannose-coated gold nanoparticles, with high-affinity binding to MBL.
The new SPR assay also provides original and validated solutions to important technical challenges (e.g. for regenerating chip, or preparing self-assembling monolayer or using complex matrices such as serum), with results that might find application in different research areas.
The paper is available Open Access on the Journal’s website.